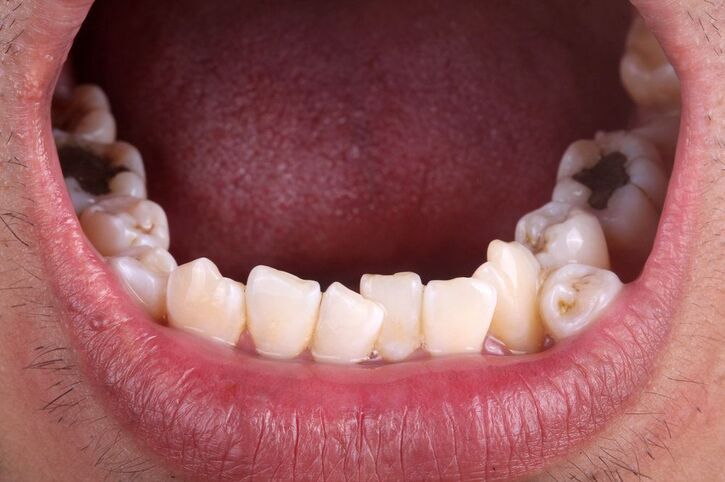
Hyperdontia is when extra teeth are in the mouth beyond the standard set of 32 permanent teeth. This condition can occur in primary and permanent dentition and affect one or more teeth. Usually, children have 20 teeth, while adults have 32 teeth. Hyperdontia is when people have more teeth than they usually have.
With hyperdontia, the number of extra teeth may be more than one. Also, according to the studies, men are more likely to develop this dental condition than women. This condition is known as supernumerary teeth as well. Both children and adults can experience it. Here is everything you need to know about hyperdontia and its signs, causes, diagnosis, and treatments.
Signs of Hyperdontia
The primary symptom of hyperdontia is extra teeth that appear in front of, behind, or next to other teeth. Mostly, the extra teeth are visible and detectable.
Another sign of hyperdontia is that you may feel pain or discomfort because of overcrowding. Typically, people with hyperdontia do not experience such problems. However, if you have multiple hyperdontia, which means you have many supernumerary teeth, you may feel these symptoms more during chewing and eating.
Causes of Hyperdontia
The exact cause of hyperdontia is unknown, but here are some associated causes of hyperdontia. Hyperdontia often relates to genetic factors. Sometimes, it may be inherited from a parent with extra teeth. Hereditary factors play an essential role in having hyperdontia.
It is also known that hyperdontia runs in families, which means that even if you do not experience this problem, your children might experience this dental condition in the future. One of the genetic conditions that cause hyperdontia is Gardner syndrome. It is a rare condition involving skeletal and dental abnormalities. Similarly, Fabry disease can lead to such overcrowding in teeth. Cleidocranial dysplasia may also cause hyperdontia. It relates to abnormal growth of the skull and collarbone. Children born with cleft palate can have hyperdontia as well. The trichorhinophalangeal syndrome is another condition that may lead to hyperdontia.
It causes distinctive facial features and skin, nails, and teeth abnormalities. Ehlers–Danlos syndrome is also known as causing dental health problems, including supernumerary teeth. Another reason for hyperdontia may be Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.
This syndrome can cause health problems, including teeth. Lastly, Nance-Horan syndrome can cause hyperdontia. Still, hyperdontia can also be related to non-genetic factors such as trauma to the mouth, infections, and certain medications. Some studies also show that medical history of some treatments or conditions can cause hyperdontia.
Different Types
Supernumerary teeth may differ according to their shape and place in the mouth. According to the position, the first of them is Mesioden. It can be located in the upper jaw, between or behind the two front teeth. It has a conical form and is more common in adult teeth than in baby teeth. The other one is called Paramolar, which can be located next to the molars. Another type of hyperdontia is Distomolar. A distomolar is a supernumerary tooth that is located back of the mouth.
Hyperdontia can be classified according to shape as well. The first one is the Conical, located near the front teeth. Another shape is called Supplemental, which is similar to the natural tooth. The other one is Compound Odontoma. In this case, the extra tooth’s shape is small. The last hyperdontia type is Complex Odontoma, a disorganised dental tissue mass.
How to Diagnose It?
Usually, it is easy to diagnose hyperdontia since having extra teeth can be easily noticed if they have already grown. The patients can notice hyperdontia by themselves, or for children, the parents or caregivers can notice it in children. However, in some cases, the diagnosis of hyperdontia is typically made through a dental examination and dental X-rays.
The dentist will check for extra teeth and determine their location and size. If necessary, the dentist may refer the patient to an oral surgeon or orthodontist for further evaluation. If the extra tooth has not grown in yet or is invisible, it can only be detected by the dentist during a dental visit. During the dental visit, the dentist will examine your mouth and jaw with dental x-rays. This way, it is possible to detect the extra tooth even if it has not yet completely grown in the jaw.
Treatment for Supernumerary Teeth
The treatment for hyperdontia depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s age. Sometimes, no treatment is necessary if the extra teeth are not causing problems. However, if the extra teeth are causing issues such as crowding or displacement of other teeth, treatment may be required. In minor cases, supernumerary teeth do not cause any problems.
If the redundant teeth are not causing any symptoms or issues, they may not need to be treated. However, you should schedule a dentist appointment if you have hyperdontia and related dental problems, such as tooth decay or toothache. If left untreated, these symptoms can lead to some significant problems in the future. Here are some of the treatment options.
The first treatment is tooth extraction. The dentist may suggest tooth or teeth extraction if you have pain and difficulty speaking or chewing because of hyperdontia. Thus, when extra teeth are removed, you can eliminate the problems associated with hyperdontia. Also, with tooth extraction, you can prevent the potential problems that supernumerary teeth will cause.
Overcrowding of teeth can lead to many dental problems, such as tooth decay, gum disease, cavities, and crooked teeth, since it can be hard to clean them properly. Due to the extra tooth’s position, cleaning between the teeth can be challenging. As a result, you may face such issues in the future.
In addition, some people may prefer tooth extraction as having supernumerary teeth also affects their appearance. People with hyperdontia may not be satisfied with the overcrowding or their smile and may want it fixed.
Another treatment for supernumerary teeth is orthodontic treatment. Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or clear aligners, may be necessary to correct any misalignment caused by the extra teeth. In addition, supernumerary teeth can affect permanent teeth and cause them to decay or break. Dental veneers, fillings, and crowns can offer medical solutions in these cases.
Also, in some cases of extreme hyperdontia, oral or jaw surgery can be recommended for the patients.
Remember to schedule a dentist appointment at least two times a year since the dentist can notice hyperdontia during a regular checkup or dental x-rays. You might still need clarification about hyperdontia.
You should see a dentist for a better answer and remedy. The dentist may recommend the best treatment to ensure your teeth are healthy. Treatments for hyperdontia are available in Smile Team. For additional information about hyperdontia and how to fix it, please visit our website or contact us.
You can reach our previous article from https://smileteamturkey.com/blog/laminate-veneers-vs-porcelain-veneers/