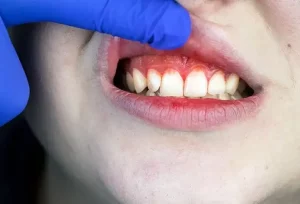
Gum disease is referred to as periodontal disease in medical terms. It can apply to the entire range of gum diseases, including gingivitis, a mild form of the illness. Even though it is most commonly used to refer to periodontitis, the more severe second stage of gum disease. Periodontal disease is one of the top ten most frequent illnesses in people, and it is the primary cause of tooth loss in adults. Therefore it’s critical to understand how it develops.
Periodontitis, a chronic inflammatory illness that affects the periodontium – the tissues, ligaments, and bones that surround and support your teeth – might develop if you don’t treat the initial stage of periodontal disease, gingivitis. Periodontitis, if left untreated, can cause serious damage to these structures, finally leading to tooth loss.
Can Periodontitis Be Cured?
Periodontitis has no known treatment. Gingivitis is the sole therapy for periodontitis while it is in its early stages, when it may be reversed before it progresses to intermediate or severe periodontitis. It can only be managed by the dentist using scaling and root planing if it has progressed to periodontal disease.
If your periodontitis is advanced, you may need a surgical procedure like as soft tissue or bone grafts. Soft tissue grafts are used to replace or strengthen your gums. When the root of your tooth is damaged, a bone graft is required. This technique improves bone development and prevents tooth loss.
What Are The 4 Stages Of Periodontal Disease?
1-Gingivitis
Gingivitis is characterized by red or swollen gums that create discomfort during brushing and flossing. Sometimes, you may detect an unpleasant breath. The growth of germs on teeth and the gum line is a common cause of gingivitis.
2- Early Stage Periodontal Disease
This indicates that an infection has extended under your gums, allowing hazardous germs to attack the bone that supports your teeth. It can be prevented from growing worse with an intensive treatment approach.
3- Moderate Periodontal Disease
The moderate periodontal disease needs more intensive treatment. To prevent plaque accumulation, surgery can restructure your gums and seal spaces between your gums and teeth. Although this may appear frightening, the prognosis is usually favorable.
4- Advanced Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease has progressed to the point of becoming irreversible. This stage is commonly treated with flap surgery, which entails washing under your gums to clean the actual roots of your teeth. To prevent germs from accumulating on weakened bone, it might be polished or sculpted.
How Do You Get Periodontitis?
Periodontal disease is caused by germs in the mouth. While there are a variety of circumstances that might contribute to the growth of these bacteria, food particles and residues of particular drinks are frequently left in the mouth. Bacteria will begin to develop and build a sticky film called plaque over the teeth and gums as a result of this. Plaque, unfortunately, contains bacteria that create acids that damage tooth enamel and gums.
The plaque will absorb minerals from saliva if left alone for long enough. It will then solidify into tartar, which will develop around the gumline. Tartar is a harsh material that makes bacteria’s surroundings even more appealing. Furthermore, tartar can only be eliminated by a trained specialist. It’s ideal to avoid tartar formation by preventing plaque development in the first place.
When plaque and tartar accumulate on the tooth surface just below the gumline, your gums become irritated, inflamed, and infected. Gingivitis is the first stage of periodontal disease and is also known as gum disease. Your gums begin to peel away from the surface of the tooth root as the periodontal disease worsens. This permits germs, food debris, and immune system waste products to build up even deeper in your gums.
The underlying jaw bone is impacted by continual inflammation as these “pockets” of diseased material along the gumline grow in size. It starts to decay, getting thinner and more porous as time goes on. It can deteriorate to the point that your teeth are no longer held firmly in their sockets.
What Happens If Periodontal Disease Goes Untreated?
As you can see, gum disease may appear to be a minor problem at first, but it may quickly escalate into something considerably more dangerous. Periodontitis left untreated can result in tooth gaps, receding gums, sensitive teeth, mouth sores, persistent poor breath, and tooth loss. Gum disease has also been linked to a number of major health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and other conditions.
The dangers of untreated gingivitis are numerous, yet treatment is straightforward, quick, and generally painless. You’ll never have to worry about untreated gum disease again if you schedule a check-up and routine cleaning with your dentist now.
How To Prevent Periodontitis?
Because the symptoms of periodontitis and advanced stages of periodontal disease are irreversible, it’s critical to create a preventative care practice before the illness worsens.
Brushing and flossing your teeth properly twice a day will eliminate plaque from your teeth and prevent build-up. To eliminate plaque from between the teeth, interdental brushes and water flossers may be useful. If you already have periodontal disease, your dentist or periodontist may advise you to visit more frequently and follow a more aggressive treatment plan.
You can read our previous article from https://smileteamturkey.com/blog/the-rhinoplasty-diet/.